Corn
Maize also known as corn , is a cereal grain ,
Maize has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat or rice. In addition to being consumed directly by humans , maize is also used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch and corn syrup.The six major types of maize are dent corn, flint corn, pod corn, popcorn, flour corn, and sweet corn.
Sugar-rich varieties called sweet corn are usually grown for human consumption as kernels, while field corn varieties are used for animal feed, various corn-based human food uses and as feedstocks for the chemical industry. Maize is also used in making ethanol and other biofuels.


Paddy
A paddy field is a flooded field of arable land used for growing semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro.
Fields can be built into steep hillsides as terraces or adjacent to depressed or steeply sloped features such as rivers or marshes. They require a great deal of labor and materials to create and need large quantities of water for irrigation.
Paddy cultivation should not be confused with cultivation of deepwater rice, which is grown in flooded conditions with water more than 50 cm (20 in) deep for at least a month.
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds.
The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa.[1] Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds.
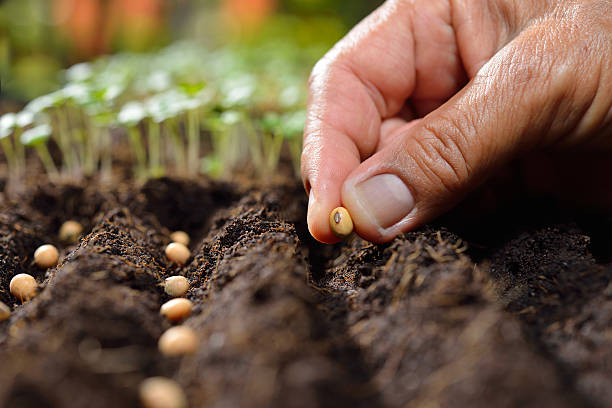


Soyabean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (Glycine max) is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes.
Soybeans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop. Soybean is the most important protein source for feed farm animals (that in turn yields animal protein for human consumption).
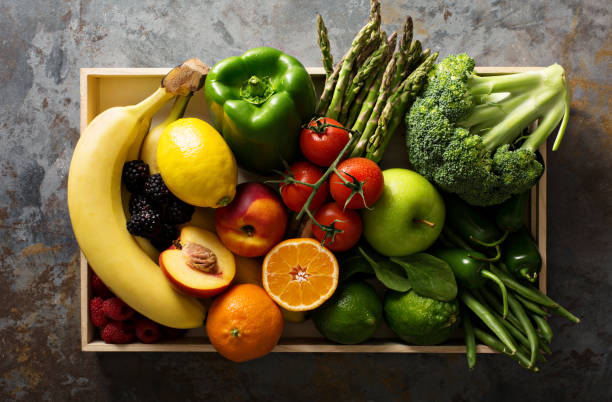
Vegetables
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, leaves, roots, and seeds.
An alternative definition of the term is applied somewhat arbitrarily, often by culinary and cultural tradition. It may exclude foods derived from some plants that are fruits, flowers, nuts, and cereal grains, but include savoury fruits such as tomatoes and courgettes, flowers such as broccoli, and seeds such as pulses.
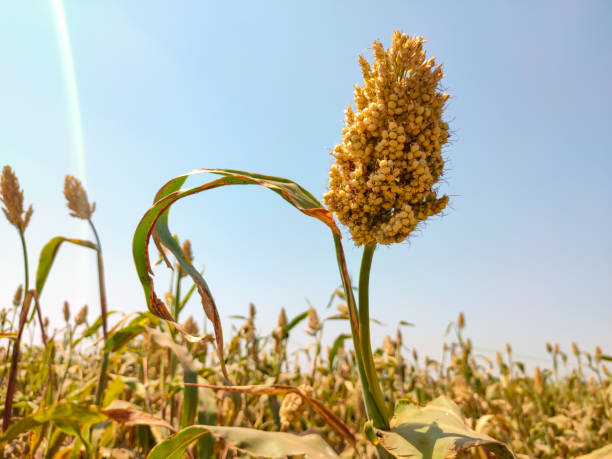


Jowar
Jowar is commonly called by various names across India- jwaarie, jowar, jola, or jondhalaa and is used to make bhakri, jowar roti, or jolada rotti. Jowar is a staple source of nutrition in areas that are arid, and it also does not need special care for growing. There are 30 varieties of Sorghum, only one of which is used for human consumption. It is the 5th most important cereal in the world.
This nutritious staple has got lost somewhere in the milieu of urbanisation, industrialisation and overdependence on refined and packaged foods. It's worth revisiting our traditional eating practices for the nutritional value it adds to daily food.
Others
The main types of seed coatings include seed dressing, film coating, and pelleting, which can be chosen differently, according to the purpose of application and the type of seed or selected microbes.
In this review, we considered seed coating as any method in which the seed surface is covered by materials forming a more or less continuous layer. Applications without the purpose of seed covering, which only comprise the use of microbial inoculants lacking any other compounds such as fillers/carriers or binders, like bacterization by seed immersion in a bacterial suspension were considered as seed treatments but not seed coating.

Copyright @ Testa Polymer technology Designed by 360 Degree Info Private Limited